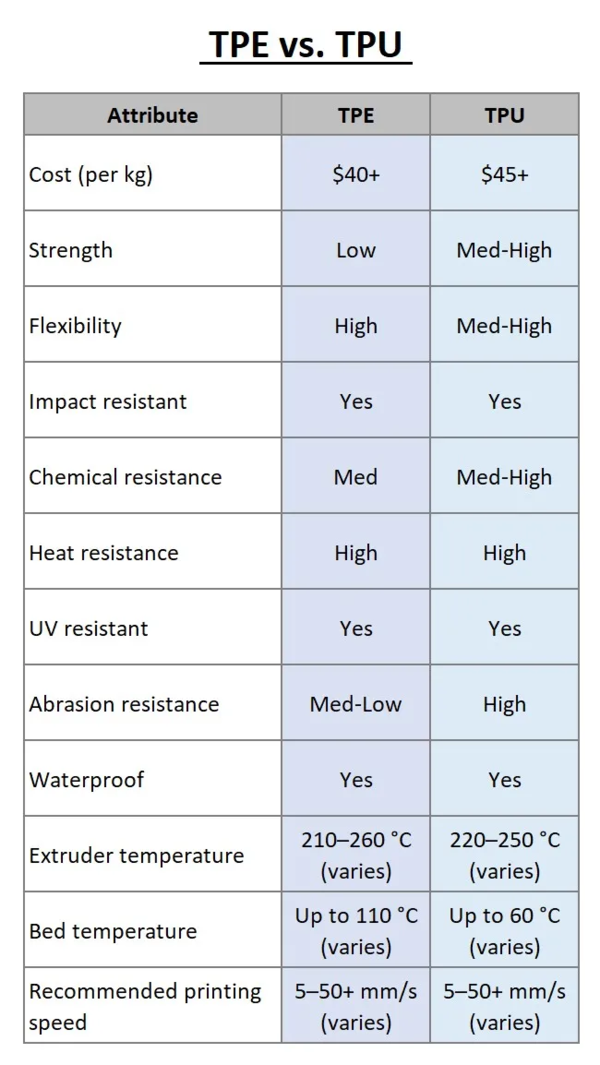
3D printing technology constructs products using a wide variety of materials, including two popular materials; Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs) and Thermoplastic Polyurethane. Both materials are reasonably priced and have many similar qualities. TPE Definition and Comparison to TPU TPE is the acronym for Thermoplastic Elastomer, a combination of rubber and plastic with both thermoplastic and elastomer properties. TPU, Thermoplastic Polyurethane, is another versatile that is derivative of TPE. Both 3D filaments produce flexible, impact-resistant, UV-resistant, impact-resistant, waterproof, and reasonably chemically-resistant parts. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are more flexible and softer to the touch. Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs) are also flexible but also more rigid. TPEs have been commercially available much longer but are relatively new in the 3D printing sector. TPEs are less expensive, have greater availability, and are best for lighter and more flexible products. TPU is preferred for more durable and rugged applications. By comparison, TPUs require less effort to 3D print, while TPE is slightly less expensive. In addition to TPU, variations of TPE include additional flexible materials, including Thermoplastic Polyamide (TPA) and Thermoplastic Copolyester (TPC). TPE is used in a variety of applications, such as automotive parts, toys, medical devices, and consumer products, such as athletic shoes and electronics. TPE is available for FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling printing as a Filament and SLS printers as a powder. The material characteristics of TPE are listed below: Good impact resistance Soft and flexible Good tear and abrasion resistance Excellent fatigue resistance Good electrical insulation properties Excellent vibration damping Good chemical and UV resistance Resistance to low and high temperatures (-30 to +140 °C) Recyclable Soft material creates extrusion problems Filament many buckle when extruded Filament is hygroscopic and should be stored properly The advantages of TPE versus TPU include the following: TPU is softer and more flexible Many TPEs can be easily recycled TPE is less expensive TPE has been available and used in products since the 1950s TPE can be printed as an intermediate layer acting as a flexible stabilizer The disadvantage of TPE versus TPU are listed below: TPE is more temperature sensitive than TPU TPEs are not as easy to print as TPUs Rework is common with TPE-printed products TPU Definition and Comparison to TPE Thermoplastic Polyurethanes (TPUs) are a derivative of TPE. It is an established material that is relatively new to 3D printing. TPU is utilized in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers as a filament and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) printers as a powder. There is a wide variety of colors, and the materials can customize hardness from soft to firm. Aerospace, automotive (i.e., instrument panels), the medical industry, industrial belts, and commercial products, including sporting goods and protective cases, utilize TPU. The material characteristics of TPU include the following: Easy to print Good impact resistance Good chemical resistance High heat resistance High tear and abrasion resistance High elasticity UV resistance is less than desirable Low print temperatures produce poor layer adhesion High print temperatures incur stringing The advantages of TPU compared to TPE include the following: In general, TPU has a smooth finish compared to the rubbery finish of TPE TPU performs better in cold temperatures and retains its elasticity better than TPE TPU has a higher degree of chemical resistance TPU maintains its dimensions better than TPE and is less prone to shrinkage TPU lasts longer due to its abrasion resistance The disadvantages of TPU, when compared to TPE, are as follows: TPU absorbs moisture (hygroscopic) Due to its performance characteristics, post-processing can be problematic Similar characteristics include: Impact resistance Heat resistance Waterproof Elasticity Excellent color selection Similar printing speeds What Are the Mutual Alternatives to TPE and TPU? The alternative to TPE and TPU is Thermoplastic Copolyester (TPC). TPC is difficult for hobbyists to obtain and is considered an engineering-grade material. TPC is a thermoplastic elastomer often used in bellows and medical stents. The material characteristics of TPC include the following: Good elasticity High strength High-temperature resistance Good thermal stability Good chemical resistance Excellent UV resistance Not advised for highly flexible applications TPC shares many of the same characteristics as TPE and TPU. They include: Thermoplastic elastomers Excellent clarity and colorability Printing speeds are similar In addition to TPC, there are other materials to compare to TPE and TPU: TPE: Silicone Elastomers – These materials have excellent thermal stability, dielectric properties, shear resistance, high compression, UV resistance, and oxidation resistance. Thermoplastic Styrene (TPS) - TPS has improved non-slip properties and is less hygroscopic. TPU: Polylactic acid (PLA) – PLA is a thermoplastic polyester popular in 3D printing since it is easier to print than TPU. Polyether Block Amide (PEBA) – PEBA is a flexible polymer filament with excellent elasticity and flexibility. Summary Currently, rubber is not 3D printable, so alternative materials like TPE and TPU are used for 3D printing. Both TPE and TPU are commonly used 3D materials. In summary: TPE is best for flexible products TPU is best for scratch and abrasion-resistant items TPE has a rubber-like finish TPU has a smoother finish TPE is difficult for printing dimensionally accurate models. TPU is more rigid and dimensionally accurate Both TPE and TPU provide good heat resistance TPE is non-toxic but releases a slight odor TPU is also non-toxic but releases noxious fumes when printing, and harmful fumes are burnt or subjected to certain chemicals Both TPE and TPU print at approximately the same speed Both TPE and TPU are environmentally-friendly and biodegradable in 3-5 years. Both TPE and TPU are similar in cost https://www.3ds.com/make/solutions/blog/tpe-vs-tpu-differences-and-comparison